Smart Contracts¶
You may see working examples of simple smart contracts:
Languages¶
In Nebulas, there are two supported languages for writing smart contracts:
They are supported by the integration of Chrome V8, a widely used JavaScript engine developed by The Chromium Project for Google Chrome and Chromium web browsers.
Execution Model¶
The diagram below is the Execution Model of the Smart Contract:
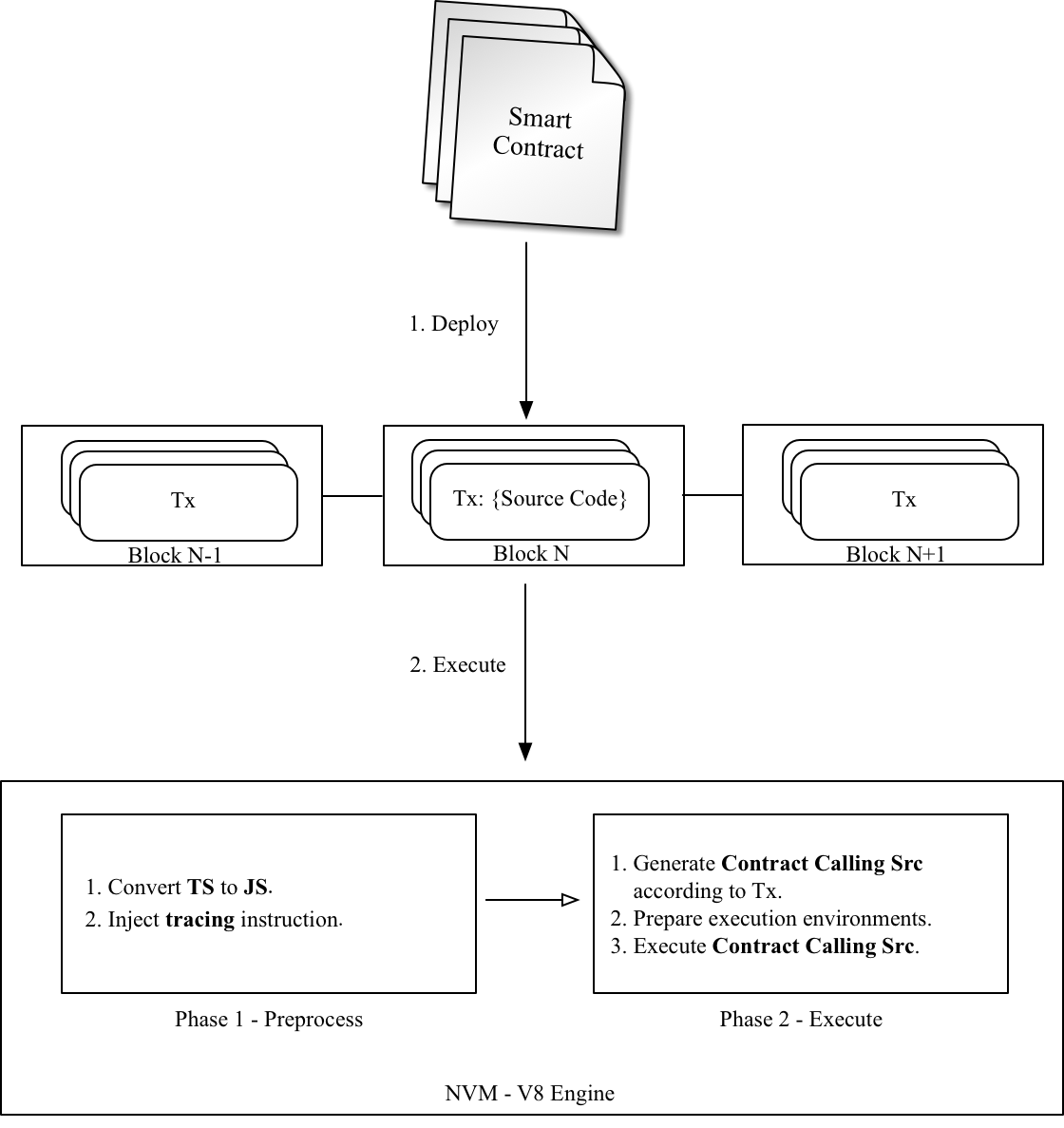
Smart Contract Execution Model
- The whole src of the Smart Contract and its arguments are packaged in the Transaction and deployed on Nebulas.
- The execution of Smart Contract is divided in two phases:
- Preprocess: inject tracing instruction, etc.
- Execute: generate executable src and execute it.
Contracts¶
Contracts in Nebulas are similar to classes in object-oriented languages. They contain persistent data in state variables and functions that can modify these variables.
Writing Contract¶
A contract must be a Prototype Object or Class in JavaScript or TypeScript.
A Contract must include an init function, it will be executed only
once when deploying. Functions whose names start with _ are
private and can’t be executed in a Transaction. The others are all
public and can be executed in a Transaction.
Since the Contract is executed on Chrome V8, all instance variables are
in memory, it’s not wise to save all of them to state
trie in Nebulas. In Nebulas, we
provide LocalContractStorage and GlobalContractStorage objects
to help developers define fields needing to be saved to state trie. And
those fields should be defined in constructor of the Contract,
before other functions.
The following is a sample contract:
class Rectangle {
constructor() {
// define fields stored to state trie.
LocalContractStorage.defineProperties(this, {
height: null,
width: null,
});
}
// init function.
init(height, width) {
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
// calc area function.
calcArea() {
return this.height * this.width;
}
// verify function.
verify(expected) {
let area = this.calcArea();
if (expected != area) {
throw new Error("Error: expected " + expected + ", actual is " + area + ".");
}
}
}
Visibility¶
In JavaScript, there is no function visibility, all functions defined in prototype object are public.
In Nebulas, we define two kinds of visibility public and
private:
publicAll functions whose name matches the regexp^[a-zA-Z$][A-Za-z0-9_$]*$are public, exceptinit. Public functions can be called via Transaction.privateAll functions whose name starts with_are private. A private function can only be called by public functions.
Global Objects¶
console¶
The console module provides a simple debugging console that is
similar to the JavaScript console mechanism provided by web browsers.
The global console can be used without calling require('console').
LocalContractStorage¶
The LocalContractStorage module provides a state trie based storage
capability. It accepts string only key value pairs. And all data is
stored to a private state trie associated with the current contract
address. Only the contract can access it.
BigNumber¶
The BigNumber module uses the
bignumber.js, a JavaScript
library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic
operations. The contract can use BigNumber directly to handle the
value of the transaction and other value transfers.
var value = new BigNumber(0);
value.plus(1);
...
Blockchain¶
The Blockchain module provides an object for contracts to obtain
transactions and blocks executed by the current contract. Also, the NAS
can be transferred from the contract and the address check is provided.
Blockchain API:
// current block
Blockchain.block;
// current transaction, transaction's value/gasPrice/gasLimit auto change to BigNumber object
Blockchain.transaction;
// transfer NAS from contract to address
Blockchain.transfer(address, value);
// verify address
Blockchain.verifyAddress(address);
properties:
block: current block for contract executiontimestamp: block timestampseed: random seedheight: block heighttransaction: current transaction for contract executionhash: transaction hashfrom: sender address of the transactionto: recipient address of the transactionvalue: transaction value, a BigNumber object for contract usenonce: transaction noncetimestamp: transaction timestampgasPrice: transaction gasPrice, a BigNumber object for contract usegasLimit: transaction gasLimit, a BigNumber object for contract usetransfer(address, value): transfer NAS from contract to address- params:
address: nebulas address to receive NASvalue: transfer value, a BigNumber object
- return:
0: transfer success1: transfer failed
verifyAddress(address): verify address- params:
address: address need to check
- return:
1: address is valid0: address is invalid
Example to use:
'use strict';
var SampleContract = function () {
LocalContractStorage.defineProperties(this, {
name: null,
count: null
});
LocalContractStorage.defineMapProperty(this, "allocation");
};
SampleContract.prototype = {
init: function (name, count, allocation) {
this.name = name;
this.count = count;
allocation.forEach(function (item) {
this.allocation.put(item.name, item.count);
}, this);
console.log('init: Blockchain.block.coinbase = ' + Blockchain.block.coinbase);
console.log('init: Blockchain.block.hash = ' + Blockchain.block.hash);
console.log('init: Blockchain.block.height = ' + Blockchain.block.height);
console.log('init: Blockchain.transaction.from = ' + Blockchain.transaction.from);
console.log('init: Blockchain.transaction.to = ' + Blockchain.transaction.to);
console.log('init: Blockchain.transaction.value = ' + Blockchain.transaction.value);
console.log('init: Blockchain.transaction.nonce = ' + Blockchain.transaction.nonce);
console.log('init: Blockchain.transaction.hash = ' + Blockchain.transaction.hash);
},
transfer: function (address, value) {
var result = Blockchain.transfer(address, value);
console.log("transfer result:", result);
Event.Trigger("transfer", {
Transfer: {
from: Blockchain.transaction.to,
to: address,
value: value
}
});
},
verifyAddress: function (address) {
var result = Blockchain.verifyAddress(address);
console.log("verifyAddress result:", result);
}
};
module.exports = SampleContract;
Event¶
The Event module records execution events in the contract. The
recorded events are stored in the event trie on the chain, which can be
fetched by FetchEvents method in block with the execution
transaction hash. All contract event topics have a chain.contract.
prefix before the topic they set in contract.
Event.Trigger(topic, obj);
topic: user-defined topicobj: JSON object
You can see the example in SampleContract above.
Math.random¶
Math.random()returns a floating-point, pseudo-random number in the range from 0 inclusive, up to, but not including 1. The typical usage is:
"use strict";
var BankVaultContract = function () {};
BankVaultContract.prototype = {
init: function () {},
game: function(subscript){
var arr =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13];
for(var i = 0;i < arr.length; i++){
var rand = parseInt(Math.random()*arr.length);
var t = arr[rand];
arr[rand] =arr[i];
arr[i] = t;
}
return arr[parseInt(subscript)];
},
};
module.exports = BankVaultContract;
Math.random.seed(myseed)if needed, you can use this method to reset the random seed. The argumentmyseedmust be a string.
"use strict";
var BankVaultContract = function \(\) {};
BankVaultContract.prototype = {
init: function () {},
game:function(subscript, myseed){
var arr =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13];
console.log(Math.random());
for(var i = 0;i < arr.length; i++){
if (i == 8) {
// reset random seed with `myseed`
Math.random.seed(myseed);
}
var rand = parseInt(Math.random()*arr.length);
var t = arr[rand];
arr[rand] =arr[i];
arr[i] = t;
}
return arr[parseInt(subscript)];
},
};
module.exports = BankVaultContract;
Date¶
"use strict";
var BankVaultContract = function () {};
BankVaultContract.prototype = {
init: function () {},
test: function(){
var d = new Date();
return d.toString();
}
};
module.exports = BankVaultContract;
Tips:
- Unsupported methods:
toDateString(),toTimeString(),getTimezoneOffset(),toLocaleXXX(). new Date()/Date.now()returns the timestamp of current block in milliseconds.getXXXreturns the result ofgetUTCXXX.
accept¶
this method aims to make it possible to send a binary transfer to a
contract account. As to is a smart contact address, which has
declared the function accept() and it excuted correctly, the
transfer will succeed. If the Tx is a non-binary Tx, it will be treated
as a normal function.
"use strict";
var DepositeContent = function (text) {
if(text){
var o = JSON.parse(text);
this.balance = new BigNumber(o.balance);//余额信息
this.address = o.address;
}else{
this.balance = new BigNumber(0);
this.address = "";
}
};
DepositeContent.prototype = {
toString: function () {
return JSON.stringify(this);
}
};
var BankVaultContract = function () {
LocalContractStorage.defineMapProperty(this, "bankVault", {
parse: function (text) {
return new DepositeContent(text);
},
stringify: function (o) {
return o.toString();
}
});
};
BankVaultContract.prototype = {
init: function () {},
save: function () {
var from = Blockchain.transaction.from;
var value = Blockchain.transaction.value;
value = new BigNumber(value);
var orig_deposit = this.bankVault.get(from);
if (orig_deposit) {
value = value.plus(orig_deposit.balance);
}
var deposit = new DepositeContent();
deposit.balance = new BigNumber(value);
deposit.address = from;
this.bankVault.put(from, deposit);
},
accept:function(){
this.save();
Event.Trigger("transfer", {
Transfer: {
from: Blockchain.transaction.from,
to: Blockchain.transaction.to,
value: Blockchain.transaction.value,
}
});
}
};
module.exports = BankVaultContract;